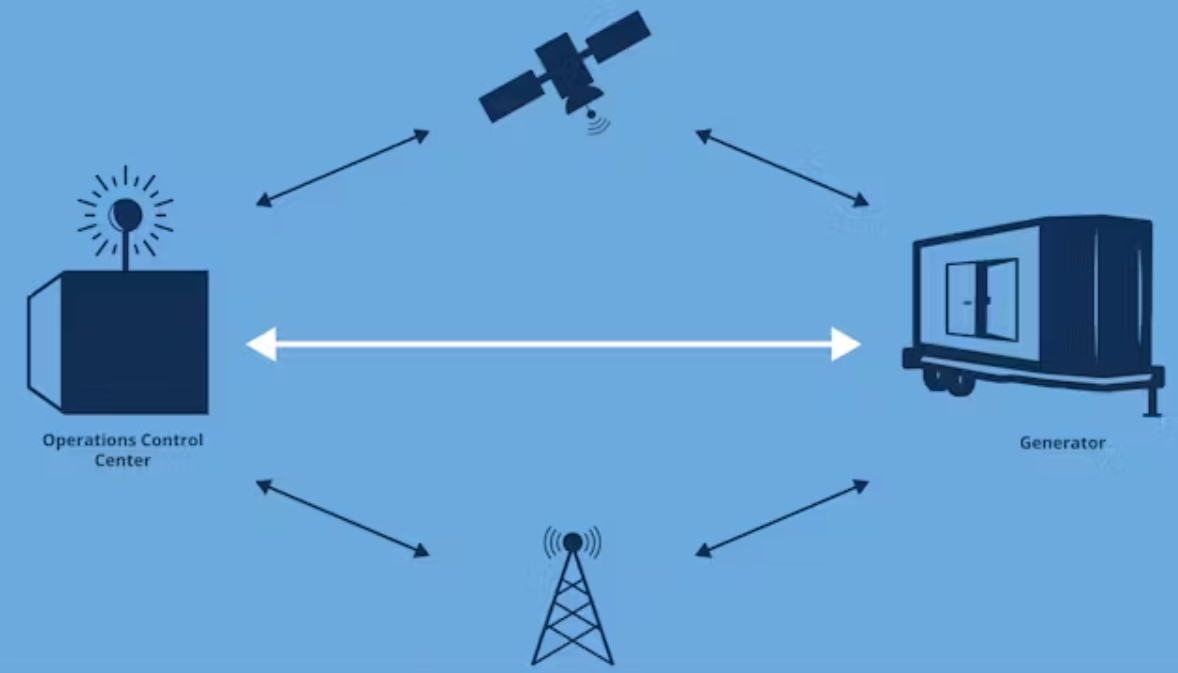
Microgrid systems are revolutionizing the way we manage and distribute energy. By integrating generators into microgrids, we can create more resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions. This comprehensive guide explores the rise of microgrid systems, their benefits, and details on top generators that can be integrated into these systems.
What is a Microgrid System?
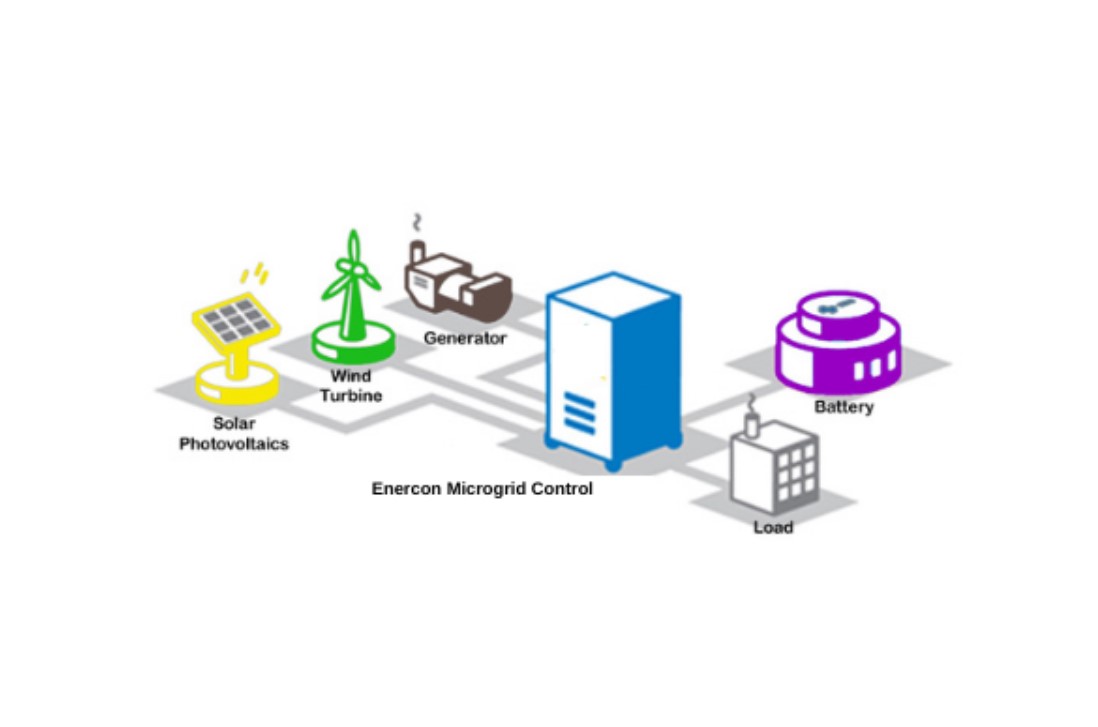
A microgrid is a localized group of electricity sources and loads that can operate autonomously from the traditional centralized grid. This ability to function independently or in conjunction with the main grid makes microgrids a flexible and reliable energy solution for a variety of applications, ranging from small residential setups to large industrial facilities. Here, we delve into the components, functionality, benefits, and different types of microgrid systems, offering a comprehensive understanding of how they work and why they are becoming increasingly important in modern energy management.
Key Components of a Microgrid System
Distributed Energy Resources (DERs)
- Renewable Energy Sources: Solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy installations are commonly used in microgrids. These sources provide clean, sustainable energy, reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Generators: Diesel, natural gas, or biogas generators serve as reliable backup power sources, ensuring continuous energy supply when renewable sources are insufficient.
- Energy Storage Systems: Batteries and other storage technologies store excess energy generated during peak production periods for use during times of low generation or high demand.
Power Management System
- Microgrid Controller: The brain of the microgrid, the controller manages the flow of electricity between different sources and loads, optimizing energy use and ensuring stability.
- Inverters and Converters: These devices convert electricity between different forms (e.g., DC to AC) and ensure that energy from various sources is compatible with the loads.
Loads
- Critical Loads: Essential services that require uninterrupted power, such as hospitals, data centers, and emergency services.
- Non-Critical Loads: Services that can tolerate temporary power loss, such as residential appliances and non-essential industrial processes.
Communication Infrastructure
- Sensors and Meters: These devices monitor energy production, consumption, and storage levels, providing real-time data to the microgrid controller.
- Communication Networks: Wireless or wired networks facilitate communication between different components of the microgrid, ensuring coordinated operation.
Functionality of Microgrid Systems
Microgrid systems are designed to operate either in grid-connected mode or islanded mode. In grid-connected mode, the microgrid interacts with the main grid, allowing for energy exchange and grid support services. In islanded mode, the microgrid operates independently, using its own energy resources to supply power to the connected loads.
Operation in Grid-Connected Mode
- Energy Exchange: The microgrid can import electricity from the main grid during periods of low renewable energy generation or high demand. Conversely, it can export excess energy back to the grid when local generation exceeds demand.
- Grid Support: Microgrids can provide ancillary services to the main grid, such as voltage regulation, frequency support, and demand response, enhancing overall grid stability and efficiency.
Operation in Islanded Mode
- Autonomous Operation: In the event of a grid outage or when the microgrid is intentionally disconnected, it operates independently, using its DERs and energy storage to supply power.
- Load Management: The microgrid controller prioritizes critical loads and manages non-critical loads to ensure that essential services receive uninterrupted power.
Types of Microgrid Systems
- Remote Microgrids:
- Applications: Ideal for remote or off-grid locations where extending the main grid is impractical or cost-prohibitive.
- Features: Rely heavily on renewable energy sources and energy storage, often supplemented by generators for reliability.
- Campus Microgrids:
- Applications: Common in university campuses, military bases, and corporate campuses.
- Features: Integrate multiple buildings and facilities, optimizing energy use and providing resilience for critical operations.
- Community Microgrids:
- Applications: Serve residential neighborhoods or small towns, enhancing local energy security and sustainability.
- Features: Focus on renewable integration and community engagement, often involving local energy markets and peer-to-peer trading.
- Commercial and Industrial Microgrids:
- Applications: Used by commercial buildings, industrial facilities, and data centers.
- Features: Provide reliable power for critical operations, optimize energy costs, and improve sustainability.
- Utility Microgrids:
- Applications: Managed by utilities to enhance grid reliability and integrate distributed energy resources.
- Features: Can operate in grid-connected or islanded mode, providing grid services and improving overall grid performance.
The Relation Between Microgrids and Generators
Generators play a critical role in microgrid systems by providing a reliable power source when renewable energy sources are insufficient or during grid outages. They act as a backup power source, ensuring continuous energy supply and enhancing the microgrid’s resilience.
Microgrid systems represent a transformative approach to energy management, offering enhanced security, sustainability, cost savings, and flexibility. By integrating diverse energy sources and advanced control technologies, microgrids provide reliable and efficient power solutions tailored to the unique needs of various applications. Whether serving remote communities, critical infrastructure, or urban neighborhoods, microgrids are poised to play a crucial role in the future of energy distribution and resilience.
Key Benefits of Microgrid Systems
Enhanced Energy Security
- Reliability: Microgrids can operate independently from the main grid, ensuring a continuous power supply during outages.
- Resilience: By incorporating multiple energy sources, microgrids are less vulnerable to disruptions.
Sustainability
- Renewable Integration: Microgrids often include renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: By managing and distributing energy locally, microgrids reduce transmission losses and improve overall efficiency.
Cost Savings:
- Reduced Energy Costs: Microgrids can optimize energy use and reduce dependence on expensive grid power.
- Economic Benefits: They can generate revenue by selling excess power back to the grid or providing grid services.
Flexibility and Scalability:
- Customizable Solutions: Microgrids can be tailored to meet the specific energy needs of a community or facility.
- Scalability: They can easily expand to accommodate growing energy demands.
Top Generators for Microgrid Systems
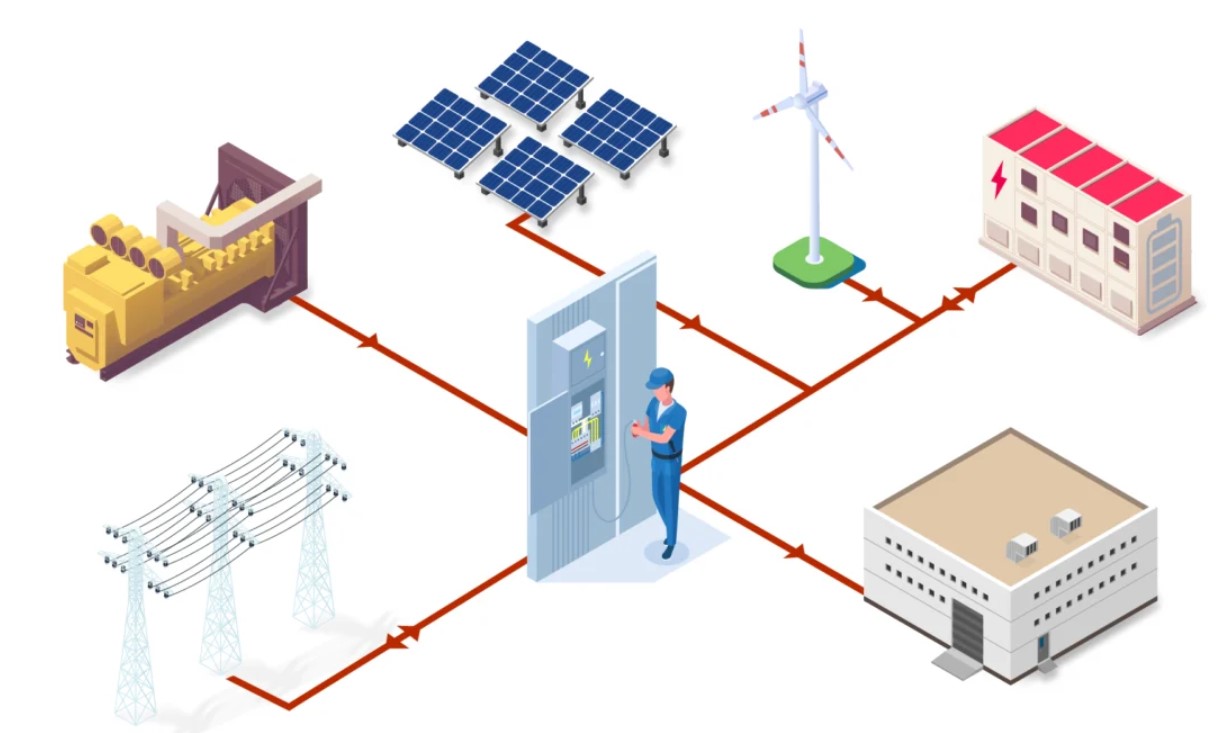
1. Cummins QSX15-G9 Generator
- Features: 500 kW capacity, high fuel efficiency, advanced control systems.
- Pros: Reliable, robust, efficient.
- Cons: High initial cost.
- Price: $50,000 – $70,000.
- Use Case: Ideal for large industrial and commercial microgrids.
2. Generac Industrial Power 750 kW Diesel Generator
- Features: 750 kW capacity, durable construction, integrated control technology.
- Pros: High power output, durable, excellent control.
- Cons: Requires regular maintenance.
- Price: $100,000 – $130,000.
- Use Case: Suitable for large-scale industrial applications and critical infrastructure.
3. Kohler 200REZXB Diesel Generator
- Features: 200 kW capacity, corrosion-resistant enclosure, low noise.
- Pros: Compact, quiet operation, corrosion-resistant.
- Cons: Moderate power capacity.
- Price: $30,000 – $40,000.
- Use Case: Best for small to medium-sized commercial and residential microgrids.
4. Caterpillar C18 ACERT Diesel Generator
- Features: 600 kW capacity, high efficiency, advanced monitoring.
- Pros: High efficiency, robust build, comprehensive monitoring.
- Cons: High operational cost.
- Price: $80,000 – $100,000.
- Use Case: Ideal for heavy-duty industrial and large commercial applications.
5. Honda EU7000iS Portable Generator
- Features: 7 kW capacity, fuel-efficient, inverter technology.
- Pros: Portable, quiet, fuel-efficient.
- Cons: Limited power output.
- Price: $4,500 – $5,500.
- Use Case: Perfect for small residential microgrids and emergency backup.
Comparison Table
| Product | Use Case | Pros | Cons | Price | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cummins QSX15-G9 Generator | Large industrial and commercial | Reliable, robust, efficient | High initial cost | $50,000 – $70,000 | 500 kW, high fuel efficiency |
| Generac Industrial Power 750 kW Diesel | Large-scale industrial, critical infra | High power output, durable | Requires regular maintenance | $100,000 – $130,000 | 750 kW, integrated control tech |
| Kohler 200REZXB Diesel Generator | Small to medium commercial, residential | Compact, quiet operation | Moderate power capacity | $30,000 – $40,000 | 200 kW, corrosion-resistant |
| Caterpillar C18 ACERT Diesel Generator | Heavy-duty industrial, large commercial | High efficiency, robust build | High operational cost | $80,000 – $100,000 | 600 kW, advanced monitoring |
| Honda EU7000iS Portable Generator | Small residential, emergency backup | Portable, quiet, fuel-efficient | Limited power output | $4,500 – $5,500 | 7 kW, inverter technology |
Detailed Benefits of Using Specific Products
Cummins QSX15-G9 Generator
The Cummins QSX15-G9 Generator is a powerhouse designed for large industrial and commercial microgrids. Its 500 kW capacity ensures that even the most demanding energy needs are met. Known for its high fuel efficiency and advanced control systems, this generator is both reliable and robust, making it a preferred choice for critical applications. Despite its high initial cost, the long-term benefits and reliability make it a valuable investment.
Generac Industrial Power 750 kW Diesel Generator
The Generac Industrial Power 750 kW Diesel Generator stands out with its high power output and durable construction. Integrated control technology allows for seamless integration into microgrid systems, providing excellent operational control. Although it requires regular maintenance, its durability and power capacity make it ideal for large-scale industrial applications and critical infrastructure.
Kohler 200REZXB Diesel Generator
The Kohler 200REZXB Diesel Generator is perfect for small to medium-sized commercial and residential microgrids. Its compact design and quiet operation make it suitable for environments where space and noise are concerns. The corrosion-resistant enclosure ensures longevity, even in harsh conditions. This generator offers a good balance of power capacity and operational quietness, making it an excellent choice for residential and small commercial setups.
Caterpillar C18 ACERT Diesel Generator
The Caterpillar C18 ACERT Diesel Generator is designed for heavy-duty industrial and large commercial applications. Its 600 kW capacity and high efficiency ensure that it can handle substantial power loads with ease. Advanced monitoring features provide comprehensive insights into the generator’s performance, enhancing operational efficiency. While the operational cost is high, the robust build and efficiency justify the investment for large-scale applications.
Honda EU7000iS Portable Generator
The Honda EU7000iS Portable Generator is a versatile option for small residential microgrids and emergency backup. Its 7 kW capacity is sufficient for essential household loads, and its fuel-efficient inverter technology ensures longer run times. The portability and quiet operation make it an excellent choice for homeowners looking for a reliable and convenient backup power solution.
Where to Buy and How to Buy
Cummins QSX15-G9 Generator
- Where to Buy: Cummins Official Website
- How to Buy: Available through authorized dealers and online stores. Ensure compatibility with your microgrid setup.
Generac Industrial Power 750 kW Diesel Generator
- Where to Buy: Generac Official Website
- How to Buy: Purchase directly from Generac or through certified distributors. Confirm specifications based on your power needs.
Kohler 200REZXB Diesel Generator
- Where to Buy: Kohler Official Website
- How to Buy: Available on Kohler’s website and authorized resellers. Check for compatibility with your microgrid requirements.
Caterpillar C18 ACERT Diesel Generator
- Where to Buy: Caterpillar Official Website
- How to Buy: Purchase through Caterpillar’s official website or authorized dealers. Ensure the product meets your industrial power needs.
Honda EU7000iS Portable Generator
- Where to Buy: Honda Official Website
- How to Buy: Available on Honda’s website and through various online retailers. Verify the generator’s suitability for your residential or emergency backup needs.
Use Cases and Problem Solving
Microgrids solve several critical issues related to energy management:
- Energy Security: By operating independently from the main grid, microgrids provide a reliable power supply during grid outages, enhancing energy security for communities and facilities.
- Sustainability: Microgrids integrate renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering carbon emissions, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Cost Management: They optimize energy use and reduce dependence on expensive grid power, leading to significant cost savings.
- Resilience: Microgrids enhance resilience by incorporating diverse energy sources and storage solutions, ensuring continuous power supply even during disruptions.
How to Buy and Where to Buy
Purchasing the right generator for your microgrid involves several steps:
- Identify Your Needs: Determine the power requirements of your microgrid system to select a generator that can handle the load.
- Research Products: Compare features, prices, and user reviews to find the best product for your needs.
- Check Compatibility: Ensure the generator is compatible with your microgrid setup.
- Purchase: Use the provided links to buy from official websites or authorized dealers.
FAQ
Q1: What is a microgrid? A1: A microgrid is a localized group of electricity sources and loads that can operate independently from the traditional grid, providing enhanced energy security and efficiency.
Q2: How do generators integrate into microgrid systems? A2: Generators serve as backup power sources in microgrid systems, ensuring continuous energy supply during periods when renewable sources are insufficient or during grid outages.
Q3: What are the benefits of using a microgrid? A3: Microgrids offer enhanced energy security, sustainability, cost savings, flexibility, and resilience, making them ideal for various applications from residential to industrial.
Q4: How do I choose the right generator for my microgrid? A4: Consider your power requirements, generator compatibility, and specific use case. Compare features, prices, and user reviews to select the best option.
Q5: Can microgrids help reduce energy costs? A5: Yes, microgrids can optimize energy use and reduce reliance on expensive grid power, leading to significant cost savings.
By following this guide, you can understand the benefits of microgrid systems and their integration with generators, providing reliable, efficient, and sustainable energy solutions. For purchasing and more information, visit the official websites linked above.