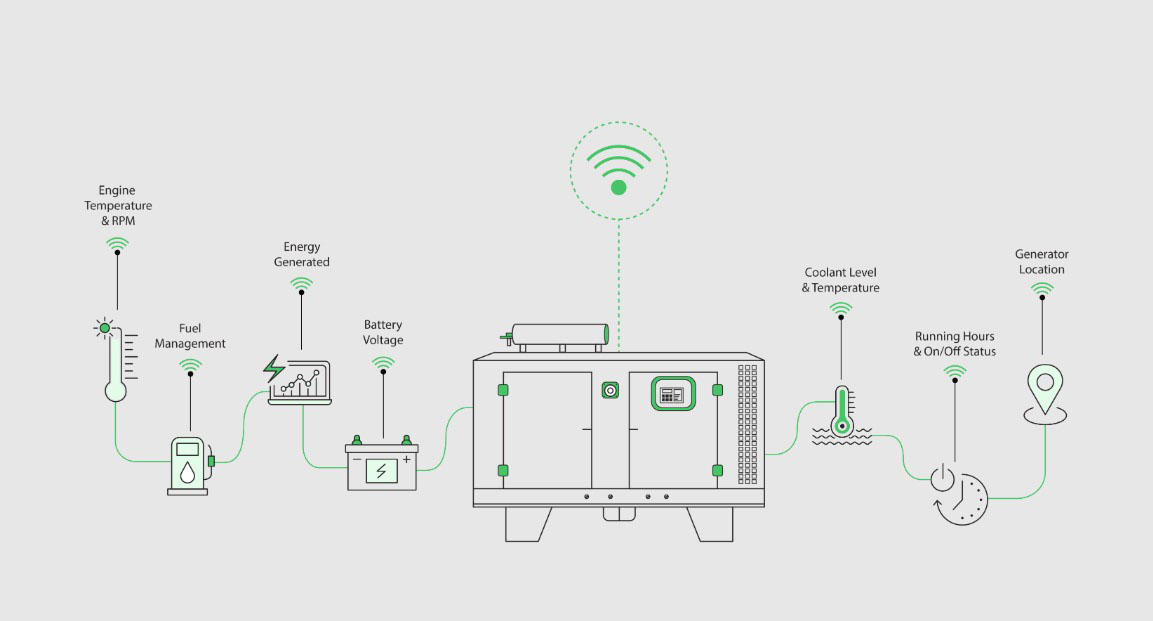
In today’s fast-paced business environment, ensuring continuous power supply is crucial. Generators provide a reliable backup power source, but their efficiency and reliability can be significantly enhanced through remote monitoring. This article explores the benefits of generator remote monitoring for businesses, providing detailed information, real-world examples, and transactional details to help you choose the best solution.
What is Generator Remote Monitoring?
Generator remote monitoring involves using advanced technology to oversee and manage generator operations from a remote location. This system collects data on generator performance, fuel levels, and potential issues, transmitting it to a central monitoring platform. This enables businesses to monitor their generators in real-time, ensuring optimal performance and timely maintenance.
Benefits of Generator Remote Monitoring
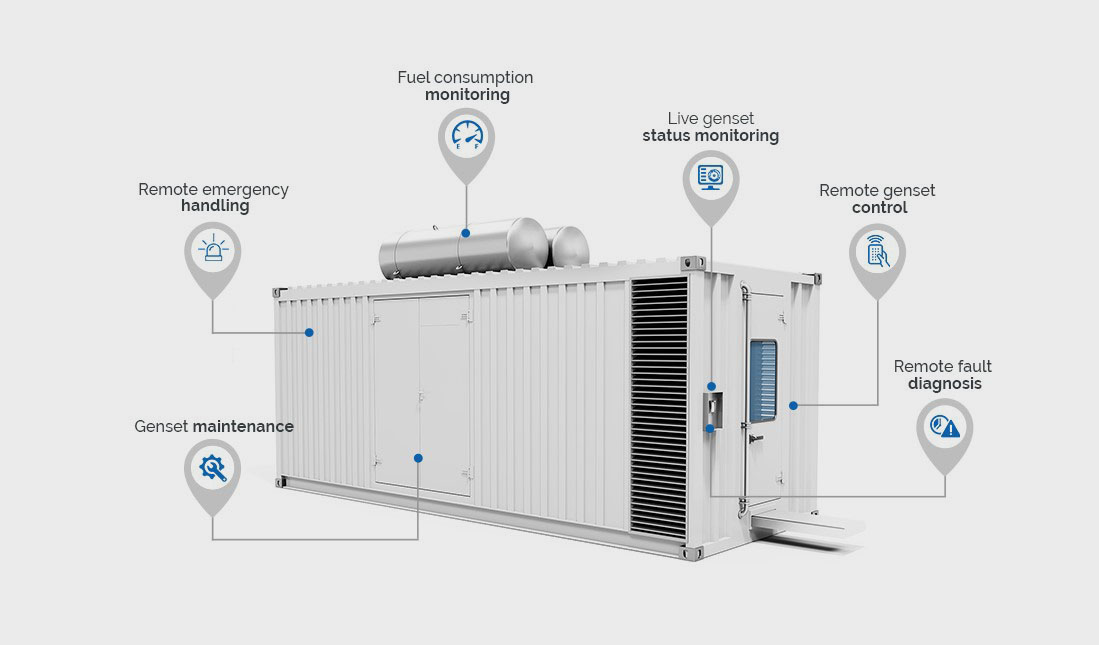
Generator remote monitoring offers numerous advantages that enhance the operational efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of power backup systems in businesses. Here is an in-depth look at the specific benefits of implementing generator remote monitoring:
1. Enhanced Efficiency
- Real-Time Monitoring: Remote monitoring systems provide instantaneous data on generator performance. This real-time insight allows for immediate detection and response to any issues that arise. Businesses can monitor metrics such as fuel levels, battery status, run hours, and overall generator health from a centralized dashboard.
- Predictive Maintenance: Utilizing advanced analytics, remote monitoring systems can predict when maintenance is required. By analyzing trends and patterns in the generator’s performance data, these systems can forecast potential failures and notify maintenance teams before issues escalate, thereby preventing unexpected breakdowns.
- Optimized Operations: With access to comprehensive performance data, businesses can optimize generator operations. This involves fine-tuning settings for optimal fuel efficiency, adjusting load management, and ensuring that generators run at peak performance levels, reducing wear and tear and extending equipment lifespan.
2. Cost Savings
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: By enabling predictive maintenance, remote monitoring helps prevent costly repairs. Addressing minor issues before they develop into major problems reduces the need for extensive repairs and replacements, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Lower Operational Costs: Remote monitoring reduces the necessity for frequent manual inspections, which can be labor-intensive and costly. Automated alerts and diagnostics allow maintenance teams to focus on scheduled and critical tasks, optimizing resource allocation.
- Minimized Downtime: Unplanned downtime can be extremely costly, impacting business operations and revenue. Remote monitoring systems minimize downtime by ensuring that generators are always in optimal working condition and ready to provide backup power when needed.
3. Increased Reliability
- Continuous Power Supply: Remote monitoring ensures that generators are always ready to provide backup power. Instant alerts for any deviations in performance or potential failures allow for quick corrective actions, ensuring continuous power supply and preventing business disruptions.
- Detailed Analytics: Comprehensive analytics provide insights into generator performance over time. Businesses can track historical data, identify recurring issues, and implement strategies to enhance reliability. This data-driven approach ensures that generators operate reliably and efficiently.
- Remote Diagnostics: Remote monitoring systems often include diagnostic tools that can identify and troubleshoot issues remotely. This capability reduces the need for on-site visits, speeds up problem resolution, and ensures that generators remain operational.
4. Enhanced Security
- Data Security: Remote monitoring systems use secure communication protocols to protect sensitive data. Encrypted data transmission ensures that performance metrics and alerts are securely sent and received, protecting against unauthorized access.
- Alert Systems: Instant alerts for any anomalies or potential issues allow for quick response and resolution. Whether it’s a sudden drop in fuel levels or a malfunction, immediate notifications enable maintenance teams to act swiftly, mitigating risks and maintaining security.
- Continuous Surveillance: Remote monitoring provides continuous surveillance of generator systems. This constant oversight helps detect any unusual activity or potential threats, ensuring the security and integrity of the power backup system.
5. Scalability
- Adaptable Solutions: Remote monitoring systems are scalable, making them ideal for businesses with growing power needs. Whether managing a single generator or a network of generators across multiple locations, these systems can be easily scaled to accommodate expanding operations.
- Centralized Management: For businesses with multiple sites, remote monitoring systems offer centralized management capabilities. This allows for efficient oversight of all generators from a single platform, ensuring consistent performance and streamlined maintenance processes.
- Future-Proofing: Investing in scalable remote monitoring solutions ensures that businesses are prepared for future growth. These systems can adapt to changing requirements, accommodating new technologies and expanding infrastructure without the need for significant upgrades.
Top Remote Monitoring Systems for Generators

Here are five top remote monitoring systems for generators, each with detailed information and comparison:
1. Cummins PowerCommand Cloud
- Features:
- Real-time monitoring and control
- Predictive maintenance alerts
- Remote diagnostics
- Pros:
- User-friendly interface
- Comprehensive data analytics
- Reliable and secure
- Cons:
- Requires internet connectivity
- Higher initial setup cost
- Price: $1,000 – $5,000 per year
2. Generac Mobile Link
- Features:
- Real-time status updates
- Maintenance reminders
- Remote monitoring via app
- Pros:
- Easy to install and use
- Affordable
- Compatible with most Generac generators
- Cons:
- Limited to Generac products
- Basic analytics features
- Price: $150 – $300 per year
3. Kohler OnCue Plus
- Features:
- Real-time monitoring and alerts
- Remote start and stop
- Maintenance scheduling
- Pros:
- Comprehensive monitoring capabilities
- Intuitive user interface
- Reliable performance
- Cons:
- Limited to Kohler generators
- Subscription required for full features
- Price: $200 – $400 per year
4. Briggs & Stratton InfoHub
- Features:
- Performance tracking
- Maintenance alerts
- Remote diagnostics
- Pros:
- Easy setup
- Detailed performance data
- Compatible with multiple generator brands
- Cons:
- Subscription required
- Limited customization options
- Price: $250 – $500 per year
5. Cat Connect
- Features:
- Advanced analytics
- Remote control and monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
- Pros:
- Highly detailed data
- Robust and reliable
- Suitable for large-scale operations
- Cons:
- Expensive
- Complex setup
- Price: $2,000 – $10,000 per year
Comparison Table
| Monitoring System | Features | Pros | Cons | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cummins PowerCommand Cloud | Real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance | User-friendly, comprehensive analytics | Requires internet, higher cost | $1,000 – $5,000/year |
| Generac Mobile Link | Real-time updates, maintenance reminders | Easy to use, affordable | Limited to Generac, basic analytics | $150 – $300/year |
| Kohler OnCue Plus | Real-time monitoring, remote start/stop | Comprehensive, intuitive interface | Limited to Kohler, subscription required | $200 – $400/year |
| Briggs & Stratton InfoHub | Performance tracking, maintenance alerts | Easy setup, detailed data | Subscription required, limited customization | $250 – $500/year |
| Cat Connect | Advanced analytics, remote control | Detailed data, robust and reliable | Expensive, complex setup | $2,000 – $10,000/year |
How to Buy the Right Remote Monitoring System for Your Business

Purchasing the right remote monitoring system for your business involves a series of well-planned steps to ensure that the chosen system meets your specific needs and provides the best return on investment. Here’s a detailed guide to help you through the process:
Step 1: Assess Your Needs
- Evaluate Your Generator Fleet: Begin by taking an inventory of the generators you have, including their models, locations, and existing monitoring capabilities. Determine how many generators need to be monitored and the extent of monitoring required (e.g., fuel levels, runtime, maintenance alerts).
- Identify Key Metrics: Identify the critical metrics and data points you need to monitor. This might include fuel levels, battery status, operational hours, load levels, and maintenance schedules. Understanding these needs will help narrow down the systems that can meet these requirements.
Step 2: Determine Compatibility
- Check Compatibility: Ensure that the remote monitoring system you are considering is compatible with your existing generators. Some systems are brand-specific, while others can work with multiple brands. Compatibility is crucial for seamless integration and functionality.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Consider how the new monitoring system will integrate with your existing infrastructure. Look for systems that can integrate with your current software and hardware to avoid unnecessary complications.
Step 3: Compare Options
- Research Systems: Look for remote monitoring systems that meet your requirements. Use online resources, manufacturer websites, and customer reviews to gather information about different systems.
- Feature Comparison: Compare the features of different systems. Key features to look for include real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance alerts, remote diagnostics, scalability, data security, and user interface quality.
Step 4: Contact Suppliers
- Reach Out for Quotes: Contact the suppliers of the shortlisted systems to request detailed quotes. Ensure that the quotes include all costs, such as initial setup, subscription fees, and any additional charges for advanced features or services.
- Ask Questions: Engage with suppliers to clarify any doubts you may have. Ask about installation procedures, training for your staff, customer support, and warranty options.
Step 5: Evaluate Costs
- Initial Setup Costs: Consider the initial setup costs, including hardware, installation, and any necessary upgrades to your existing infrastructure.
- Ongoing Costs: Evaluate ongoing costs such as subscription fees, maintenance charges, and any costs associated with software updates or additional features.
- Total Cost of Ownership: Calculate the total cost of ownership over the expected life of the system. This includes both initial and ongoing costs, helping you understand the long-term financial commitment.
Step 6: Assess Vendor Reliability
- Vendor Reputation: Research the reputation of the vendors. Look for established companies with a track record of reliability and good customer service. Customer testimonials and case studies can provide valuable insights.
- Future Support and Upgrades: Consider the vendor’s commitment to future support and upgrades. A good vendor will offer ongoing support and regularly update their systems to incorporate new technologies and features.
Step 7: Pilot Testing
- Request a Demo: If possible, request a demonstration or trial period to test the system. This hands-on experience can help you evaluate the user interface, ease of use, and overall functionality.
- Pilot Implementation: Implement the system on a small scale initially, such as with a single generator or a small group of generators. Monitor its performance and gather feedback from your team.
Step 8: Finalize Purchase
- Review Terms and Conditions: Carefully review the terms and conditions of the purchase, including any service level agreements (SLAs) and warranty terms.
- Negotiate: Negotiate the final terms to ensure you get the best possible deal. This might include price reductions, extended warranties, or additional support services.
- Complete the Purchase: Once you are satisfied with the terms, complete the purchase and schedule the installation and setup of the system.
Step 9: Implementation and Training
- Professional Installation: Arrange for professional installation of the monitoring system. Ensure that all components are correctly installed and configured for optimal performance.
- Staff Training: Provide comprehensive training for your staff on how to use the monitoring system. This should include understanding the interface, interpreting data, and responding to alerts.
Step 10: Monitor and Optimize
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor the performance of your generators using the remote monitoring system. Use the data to optimize generator operations and maintenance schedules.
- Feedback and Improvements: Gather feedback from users and make necessary adjustments to improve the system’s effectiveness. Regularly review performance data and updates from the vendor to ensure you are leveraging the system’s full potential.
Use Cases and Problem-Solving
Ensuring Continuous Operations
Example: A large data center relies on generator remote monitoring to ensure uninterrupted operations during power outages. By using a remote monitoring system, they can detect issues early, schedule maintenance proactively, and avoid costly downtime.
Reducing Maintenance Costs
Example: A manufacturing plant implements generator remote monitoring to optimize maintenance schedules. Predictive maintenance alerts allow them to address potential issues before they become major problems, reducing overall maintenance costs.
Enhancing Security
Example: A financial institution uses generator remote monitoring to enhance the security of their operations. The system provides real-time alerts for any anomalies, allowing for quick response and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
Improving Efficiency
Example: A hospital implements a remote monitoring system for their backup generators. The real-time data and analytics help them optimize generator performance, ensuring that critical medical equipment remains operational during power outages.
Scalability for Growing Businesses
Example: A retail chain uses remote monitoring to manage generators across multiple locations. The scalable solution allows them to monitor all their generators from a central platform, ensuring consistent performance and reliability across their operations.
FAQs
1. What is generator remote monitoring?
Generator remote monitoring is a system that uses advanced technology to oversee and manage generator operations from a remote location, providing real-time data on performance, fuel levels, and potential issues.
2. How does remote monitoring improve generator efficiency?
Remote monitoring improves efficiency by providing real-time data, enabling predictive maintenance, and optimizing operations through detailed analytics.
3. Are remote monitoring systems expensive?
The cost of remote monitoring systems varies, with prices ranging from $150 to $10,000 per year, depending on the features and capabilities.
4. Can remote monitoring systems work with any generator?
Many remote monitoring systems are compatible with multiple generator brands, but some may be limited to specific brands. It’s important to check compatibility before purchasing.
5. How do I choose the right remote monitoring system for my business?
Assess your specific needs, compare different systems based on features and costs, and contact suppliers for detailed information and quotes to make an informed decision.
By leveraging the power of generator remote monitoring, businesses can enhance efficiency, reliability, and security, ensuring continuous operations and significant cost savings.